Preventative Maintenance (PM) is a key component within an Asset Management strategy. The ability to maintain equipment at optimal levels requires careful orchestration between several people and systems. Complexities are added when portions of the maintenance agreement is sub-contracted out to other vendors.
Preventative Maintenance ensures peak efficiency and minimizes deterioration of a piece of equipment. Recurring service tasks are generated, assigning the right technician with the right availability and skills set. Regardless if the work is completed by an in-house technican or through subcontractors, the ability to capture work details in the field is key.
Basic mobility is need for collecting time and expense information, as well as, for filling out forms and check lists. Many service-companies choose to perform their mobile tasks through web browsers tethered to a “hot spot” instead of a true mobile application. This allows for device flexibility while providing a secure environment to enter customer specific data.
Optimize PM Schedules through PM Batches. If you perform hundreds or thousands of PM Schedules per year, you may opt to do batched PMs. This eliminates the need to adjust reports on “Open Cases” and minimizes a bog down in the Incident queue.
Companies evaluating Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) and CMMS rank Preventative Maintenance as a Top 10 functional requirement. The Chart is taken from Technology Evaluation Centers (TEC) 2013 Market Survey Report.
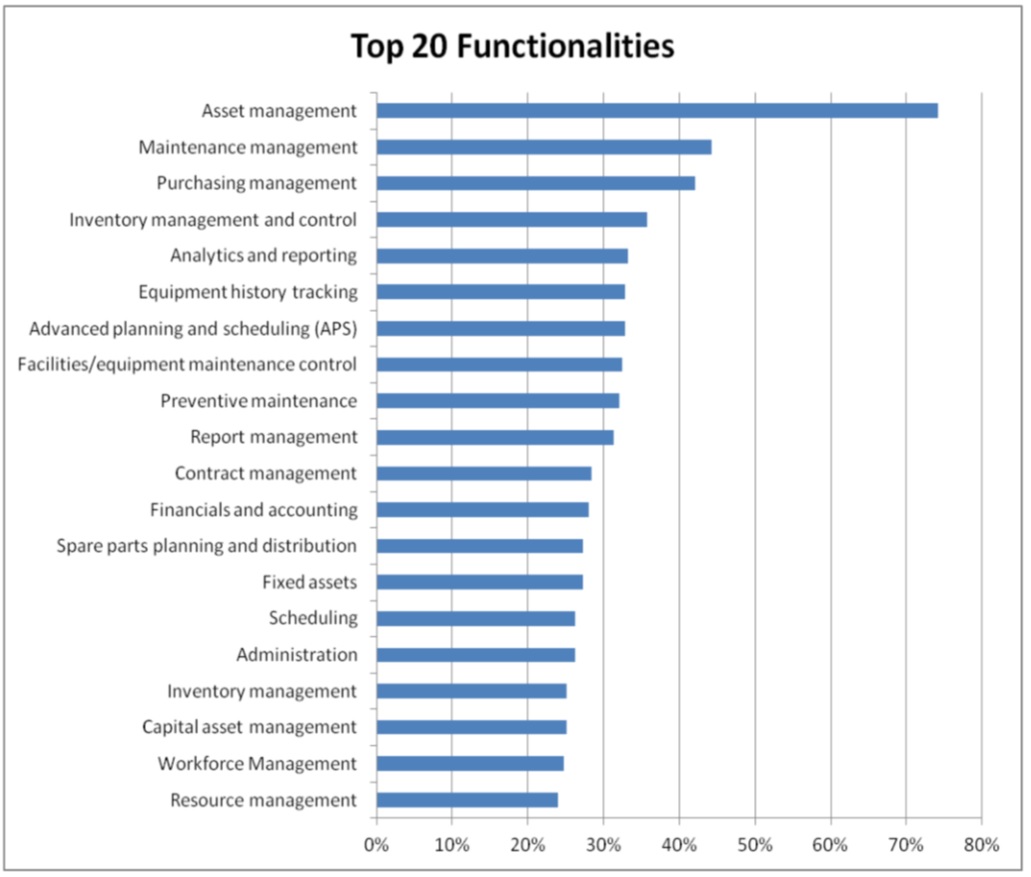
Top 20 EAM and CMMS Strategies by TEC 2013 Report
